```html
Standard Bathroom Pipe Size: A Comprehensive Guide
When undertaking plumbing work in a bathroom, whether it involves a new installation, renovation, or simple repair, understanding standard bathroom pipe sizes is crucial. Correct pipe sizing ensures efficient water flow, prevents pressure problems, and avoids potential leaks and damage. Ignoring these standards can lead to costly repairs and inconvenience in the long run. This article provides a comprehensive guide to standard bathroom pipe sizes, covering various fixtures and common plumbing materials, highlighting the importance of adhering to these standards for optimal plumbing performance.
Understanding the Importance of Correct Pipe Sizing
Proper pipe sizing within a bathroom's plumbing system is paramount for several reasons. If the pipe diameter is too small, it can restrict water flow, leading to low water pressure at the showerhead or faucet. This can result in a frustrating user experience, especially during peak usage times. Conversely, excessively large pipes can lead to wasted water and energy, as it takes more time and energy to heat and transport the larger volume of water within them.
Furthermore, incorrect pipe sizing can contribute to plumbing system imbalances. This means that one fixture may draw water excessively from another, leading to fluctuations in water pressure and temperature. For example, flushing a toilet might cause a sudden drop in shower water pressure if both fixtures are sharing an inadequately sized water supply line. This lack of balance creates an unpleasant and inefficient plumbing system.
Finally, improper sizing can promote corrosion and scale buildup. Slow water flow in oversized pipes allows sediment and minerals to settle, potentially leading to corrosion and restricted water flow over time. The accumulation of scale within piping can further reduce the inner diameter, exacerbating the pressure issues that initially resulted from incorrect sizing. Therefore, selecting the correct pipe size is essential for maintaining optimal water pressure, minimizing water wastage, and preventing long-term plumbing problems.
Standard Pipe Sizes for Bathroom Fixtures
The plumbing code, often based on the Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) or International Plumbing Code (IPC), typically dictates the required pipe sizes for various bathroom fixtures. These standards aim to ensure adequate water supply and drainage for each fixture. Deviation from these standards can result in code violations and potentially unsafe plumbing conditions.
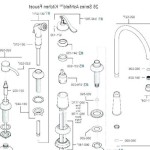
For toilet supply lines, a ½-inch pipe is commonly used. This size provides sufficient water flow for quick and efficient toilet flushing. However, the drain line, or soil pipe, for a toilet is significantly larger, typically 3 or 4 inches in diameter. The larger diameter is necessary to accommodate the solid waste and water discharged during flushing and to prevent clogs within the drainage system.
Bathroom sinks generally use a ½-inch supply line for both hot and cold water. The drain line from the sink typically requires a 1 ¼-inch or 1 ½-inch diameter pipe. The exact size often depends on the sink's drain fitting configuration and the local plumbing codes.
Showers and bathtubs also use ½-inch supply lines for both hot and cold water. However, high-flow showerheads may benefit from a ¾-inch supply line to maintain adequate water pressure. The drain line for a shower or bathtub is typically 1 ½ or 2 inches in diameter to ensure proper drainage and prevent water from pooling during use.
It's important to note these are general guidelines. Local plumbing codes may specify different requirements. Consulting a licensed plumber ensures all pipe sizes comply with local regulations, preventing potential problems later.
Common Plumbing Materials and Their Sizing Considerations
Various materials are used for plumbing in bathrooms, each with its own advantages and disadvantages regarding sizing, installation, and compatibility. Understanding these material properties is essential when selecting the appropriate piping for a project.
Copper piping has been a traditional choice for decades due to its durability, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand high water pressure and temperatures. Copper pipes are available in various types, including Type M (thin-walled), Type L (medium-walled), and Type K (thick-walled). Type L is the most common choice for residential plumbing due to its balance of strength and cost-effectiveness. When working with copper, it is important to understand that the stated size is the nominal size, which does not directly correspond to the actual inner or outer diameter of the pipe. Copper pipes are joined using soldering or compression fittings, which require precise measurements and proper techniques to ensure leak-free connections.
PEX (Cross-linked Polyethylene) is a flexible plastic piping option that has become increasingly popular due to its ease of installation, resistance to freezing, and lower cost compared to copper. PEX piping is available in various colors, typically red for hot water and blue for cold water, which simplifies identification. PEX is also sized nominally, and it is important to verify the inner diameter to ensure adequate flow rates. PEX connections are made using crimp rings, expansion fittings, or push-fit fittings, each requiring specific tools and techniques.
CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) is another type of plastic piping used primarily for hot water distribution. CPVC has a higher temperature tolerance than standard PVC and can withstand temperatures up to 180 degrees Fahrenheit. CPVC is often joined using solvent cement, which creates a strong, leak-proof bond. CPVC piping is also sized nominally, similar to copper and PEX.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) are commonly used for drain, waste, and vent (DWV) systems. ABS is typically black, while PVC is white or gray. ABS is more resistant to impact, while PVC is more resistant to chemicals. Both ABS and PVC are relatively inexpensive and easy to install using solvent cement. DWV pipes are also sized nominally. When selecting piping materials, it’s crucial to consider local building codes and the specific application to ensure compliance and optimal performance.
When selecting pipe materials, it's also important to consider the fittings used to connect them. The fitting's inner diameter should match the pipe's inner diameter to minimize flow restriction. Transitions between different pipe materials, such as copper to PEX, require special fittings designed for that purpose. Failure to use the correct fittings can lead to leaks, corrosion, and other plumbing problems.
```
Pin On Outdoors

Top 35 Useful Standard Dimensions House Bathroom Designs Design Small Layout

Standard Height Of Bathroom Fittings Fantasticeng

Standard Height Of Plumbing Fixtures Detailed Information Civil Site
:strip_icc()/SCP_173_04-a5f887244add47e48d7a24d0579341d7.jpg?strip=all)
The Ultimate Guide To Bathroom Plumbing Diagrams And Layouts

Standard Height Of Plumbing Fixtures Detailed Information Civil Site

Standard Bathroom Rules And Guidelines With Measurements Engineering Feed

Standard Bathroom Sizes Dimensions Design Small

How To Plumb A Toilet Vent Distance Pipe Size

The Standard Height For Shower Plumbing Installation Bathroom
Related Posts